Date :
2005
State of progress :
Ended
Objectives :
Study of the effects of space flight on the human body and Nutritional and exercise countermeasures
Partners :
CNES, ESA, NASA, CSA
The WISE (Women International Space Simulation for Exploration) study, conducted in 2005-2006, was a bed rest study of 24 female volunteers who stayed 100 days at the Toulouse Space Clinic, 60 of which were spent lying down to simulate the effects of weightlessness.
The study took place in two sessions: from April to June 2005 for the first 12 volunteers, and from September to December for the other 12.
This bed rest study was organised by MEDES for the French, European, American and Canadian Space Agencies (CNES, ESA, NASA and CSA).
An essential study to advance research
As space flight is not a common occurrence, ground-based studies are essential to prepare for long-duration crewed flights.
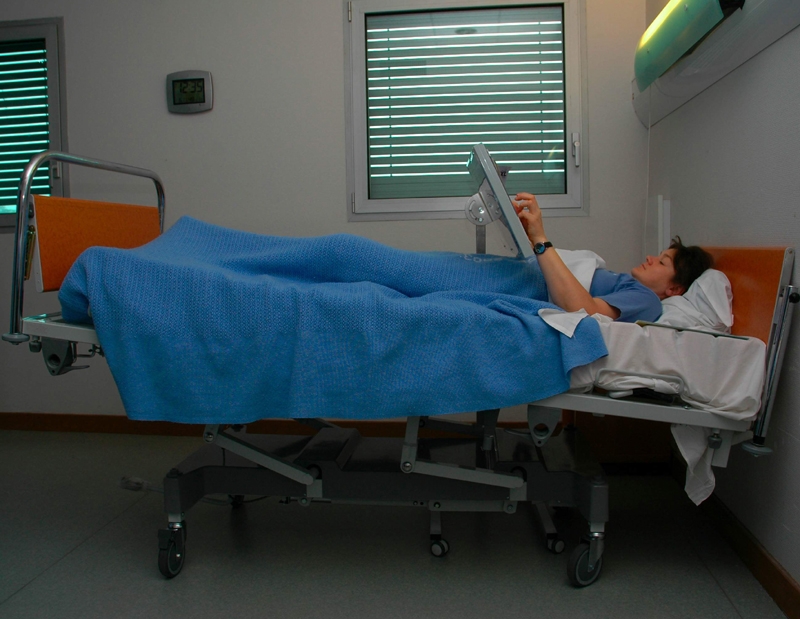
Twenty-four female volunteers took part in this study for 100 days, staying for 60 days with their bodies slightly tilted downwards (-6°) to simulate the physiological effects of a prolonged stay in weightlessness.
MEDES regularly conducts bed rest experiments but this was the first long-term experiment with female volunteers.




The aim of the experiment was to investigate the extent to which diet and exercise can counteract the adverse effects of the prolonged absence of gravity, simulated by these bed rest conditions.
The volunteers who took part in the study came from France, Great Britain, Germany, Finland and the Netherlands, but also from Poland and the Czech Republic, a sign of the considerable interest in the WISE study among the new Member States of the European Union.
Objectives of the study
The aims of the study were to assess the consequences of a long, simulated flight and to test the effectiveness of the countermeasures used.
Internationally renowned scientific teams followed protocols to monitor the following :
- Physical capacity,
- Heart function and blood circulation,
- Blood measurements,
- Muscle structure and function, Bone structure and function,
- Energy and nutritional requirements,
- Immune system,
- Hormonal regulation and the reproductive cycle,
- Reflexes and balance,
- Mood and well-being.
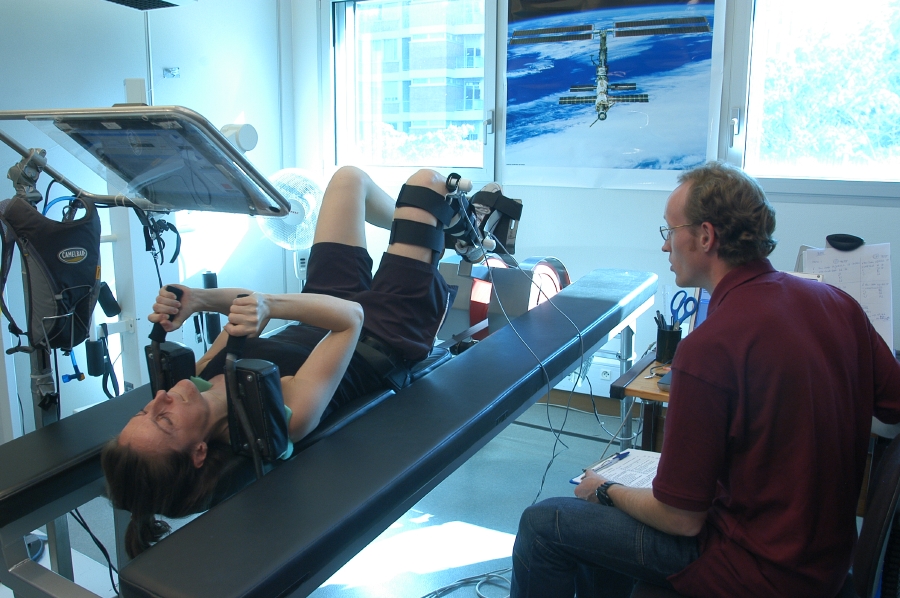

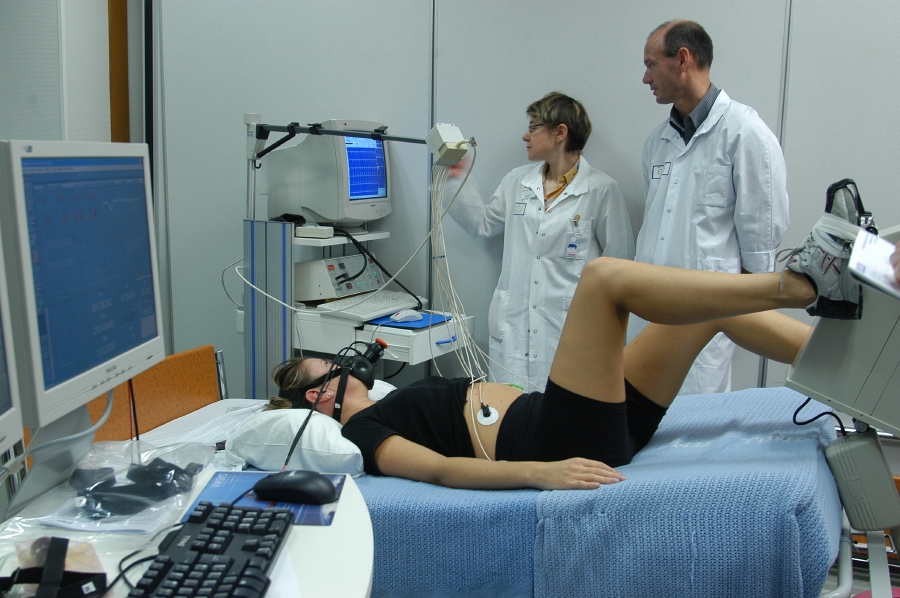
Study configuration
The WISE study was carried out in two successive campaigns, each involving 12 volunteers.
The volunteers were randomly divided into three groups:
- One group served as a control group and received no countermeasures.
- One group performed a combination of physical exercises while remaining in bed.
- The third group received a nutritional supplement.
The results are intended to be compared with those obtained by astronauts during space flights.
The study lasted 101 days, of which 60 days were spent in the supine position, broken down as follows :
- The first phase of the study consisted of volunteers undergoing a series of tests to collect basic physiological data to serve as a reference throughout the study.
- At the end of this 20-day preliminary observation phase, the actual bed rest phase took place. During this phase the volunteers were subjected to a series of examinations and tests according to the various study protocols. During this bed rest phase, the volunteers had to remain in the head down position (6° below the horizontal) without getting up, neither for meals nor for washing. Only those movements that kept the body axis in this position were allowed. In addition to the tests, the volunteers’ days were also interspersed with leisure time. Volunteers were given access to television, internet or telephone to talk to their relatives and friends. They also had the opportunity to take language classes, enjoy beauty treatments… and even had a visit from Claudie Haigneré, astronaut and former Minister for European Affairs, and Jean-François Clervoy and Pedro Duque, astronauts.
- During the 20 days following the bed rest phase, the volunteers underwent tests identical to the first phase, the results of which were compared with reference data.

Nos actualités
Nos projets
Une question ?
Devenir volontaire ?
Nos études cliniques
Urgent ! Recrutement volontaires
